In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, efficiency is key. Low pressure molding machines stand out for their versatility and effectiveness. According to industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, "The right low pressure molding machine can revolutionize production lines." This statement highlights the significant impact these machines have on operations.
Low pressure molding machines offer advantages in various applications. They reduce waste and improve product consistency. However, not all machines deliver the same results. Some models falter in reliability, leaving room for improvement. Careful selection is essential to maximize benefits.
While many options exist, understanding specific needs is crucial. Choosing a low pressure molding machine can be daunting. Manufacturers must evaluate features and performance. Balancing cost with quality is often a challenge. This decision shapes production efficiency and outcomes. Reflecting on these aspects can lead to better choices in the future.
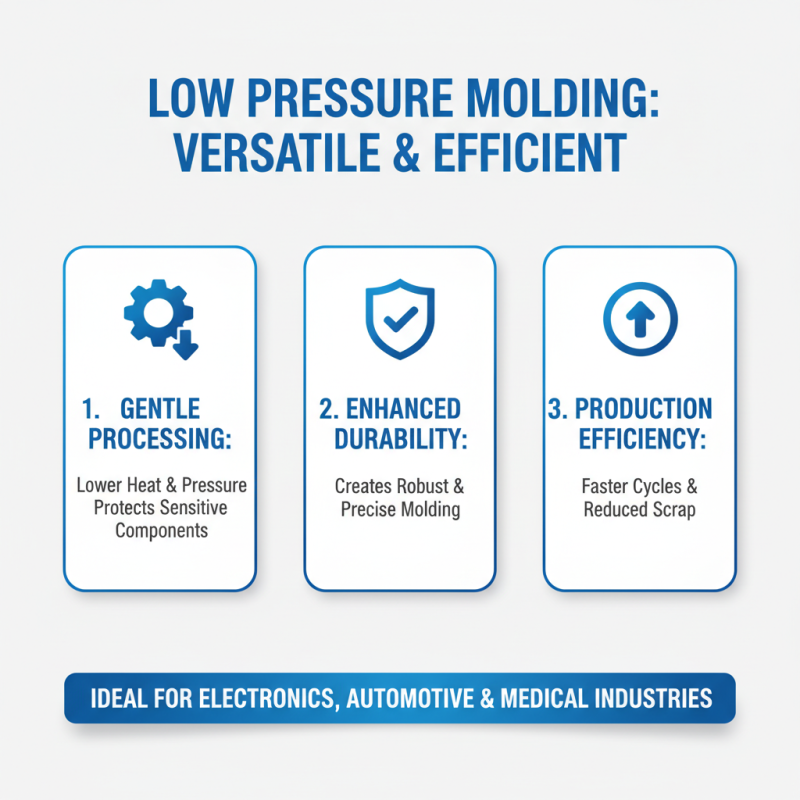
Low pressure molding machines offer a versatile solution for various industries. They provide unique benefits that enhance production efficiency. These machines are designed to create durable and precise molding by using lower temperatures and pressures. This reduces the risk of thermal damage to sensitive components.
One major advantage is material savings. Low pressure molding minimizes waste by using just the right amount of material. Moreover, the process can often be completed faster than traditional methods. Moldings made with these machines have a smoother finish. Yet, it is essential to consider the learning curve involved. Operators may need time to understand the machine's settings fully.
Another aspect is the flexibility of design. Low pressure molds can accommodate intricate shapes easily. However, achieving perfect results every time can be tricky. Calibration issues might lead to inconsistencies in product quality. Everyone involved must be vigilant to catch any potential errors during production. Adjustments may take time, but they are crucial for optimal output.
Low pressure molding machines are gaining traction in various industries due to their efficiency and versatility. A recent industry report reveals that the global low pressure molding market is expected to grow by 6.7% annually. This growth is driven by increased demand for lightweight materials and complexity in product designs.
Key features of top low pressure molding machines include advanced temperature control and energy-efficient systems. These machines can precisely manage the heating and cooling phases, ensuring optimal production cycles. Furthermore, automation features enhance production rates and reduce labor costs. For instance, machines with integrated robots can efficiently handle repetitive tasks without compromising quality.
However, not every machine excels in all areas. Some models may have limited compatibility with specific materials, posing challenges during production. Others might require constant calibration to maintain efficiency. The industry also faces scrutiny concerning energy consumption. Striking a balance between performance and sustainability remains an ongoing challenge. Thus, manufacturers must continually innovate and adapt to meet evolving market demands.
This chart illustrates the production efficiency of the top 10 best low pressure molding machines available in the market, showcasing how each machine performs in terms of units produced per hour.
The low pressure molding market is experiencing significant growth. According to a recent industry report, the global market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is driven by increasing demand from various sectors, including automotive and electronics. Manufacturers are seeking efficient production methods that reduce waste and enhance product durability.
Furthermore, the rise in electric vehicle production is influencing low pressure molding needs. Reports indicate that nearly 30% of automotive manufacturers are adopting this technology to create lightweight components. These trends highlight a shift in production techniques, emphasizing efficiency and sustainability. Companies face challenges in optimizing processes, and they need to adapt quickly.
In addition, the electronics sector's rapid evolution requires precision molding solutions. With a 15% annual growth in consumer electronics, investments in advanced molding technologies are critical. However, many manufacturers struggle with integrating these systems effectively. The need for skilled operators and proper training remains a significant hurdle. Addressing these issues will be essential for capitalizing on the expanding market opportunities.

When comparing efficiency metrics among low pressure molding machines, it’s crucial to consider various factors. Production speed, energy consumption, and cycle times are vital parameters. Recent industry reports highlight that machines specifically designed for low pressure molding can reduce cycle times by up to 30%. This efficiency can significantly lower operational costs, making it attractive for manufacturers.
Tip: Regular maintenance can enhance the efficiency of low pressure molding machines. Neglect can lead to increased downtime and higher energy use. Operators should be trained to identify minor issues early.
Not all machines perform equally under pressure. Some may struggle during high-demand periods, leading to inconsistencies. Industry data suggests that a balanced approach to load management can prevent these pitfalls. Understanding your production needs is essential for optimal machine selection.
Tip: Evaluate the machine’s performance metrics before purchase. Collect data from multiple sources to make informed decisions. Avoid relying solely on manufacturer claims. Real-world performance may differ significantly.
Low pressure molding technology has transformed various industries. It offers a unique blend of efficiency and precision. One case study showcases its application in the automotive sector. By using low pressure molding, a manufacturer enhanced the durability of electronic components. This reduced the risk of failure due to environmental factors.
In another instance, the medical industry benefited significantly. A facility employed low pressure molding to produce sensitive devices. The process ensured that components were encapsulated without stress or damage. This improved product reliability, meeting strict regulatory standards. However, challenges arose. The team faced initial setup issues. Adjusting parameters took time and experimentation.
These examples highlight the practical benefits of low pressure molding technology. It illustrates how production efficiency can combine with product integrity. Yet, there is always room for improvement. Each case reminds us to analyze processes continuously. This is essential for long-term success.
| Machine Model | Production Capacity (units/hour) | Max Mold Size (mm) | Heating Method | Cycle Time (minutes) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 100 | 500 x 300 | Electric | 3 | Automotive parts |
| Model B | 120 | 600 x 400 | Gas | 4 | Consumer electronics |
| Model C | 80 | 450 x 300 | Steam | 5 | Medical devices |
| Model D | 150 | 700 x 500 | Electric | 3.5 | Aerospace components |
| Model E | 90 | 480 x 320 | Gas | 6 | Telecommunications |
| Model F | 110 | 600 x 400 | Electric | 4.5 | Industrial appliances |
| Model G | 130 | 750 x 500 | Steam | 3 | Home appliances |
| Model H | 70 | 400 x 250 | Gas | 6.5 | Small electronic devices |
| Model I | 140 | 700 x 400 | Electric | 3.2 | Robotics |
| Model J | 100 | 500 x 300 | Gas | 5 | Construction materials |






