In the realm of manufacturing, low pressure injection molding has emerged as a pivotal technique, particularly in industries such as automotive and consumer goods, where precision and efficiency are paramount. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for injection molding is projected to reach USD 364.5 billion by 2025, with low pressure techniques gaining traction due to their ability to produce high-quality parts with minimal waste. This method not only reduces the stresses on the material being molded, ensuring better structural integrity, but also allows for lower cycle times and energy consumption compared to traditional high-pressure methods. By mastering low pressure injection molding, manufacturers can achieve optimal results that meet the growing demands for sustainable and cost-effective production solutions. As we delve into the specifics of this technique, we will explore key strategies and best practices that can enhance the proficiency of engineers and operators alike, ultimately driving innovation in the industry.
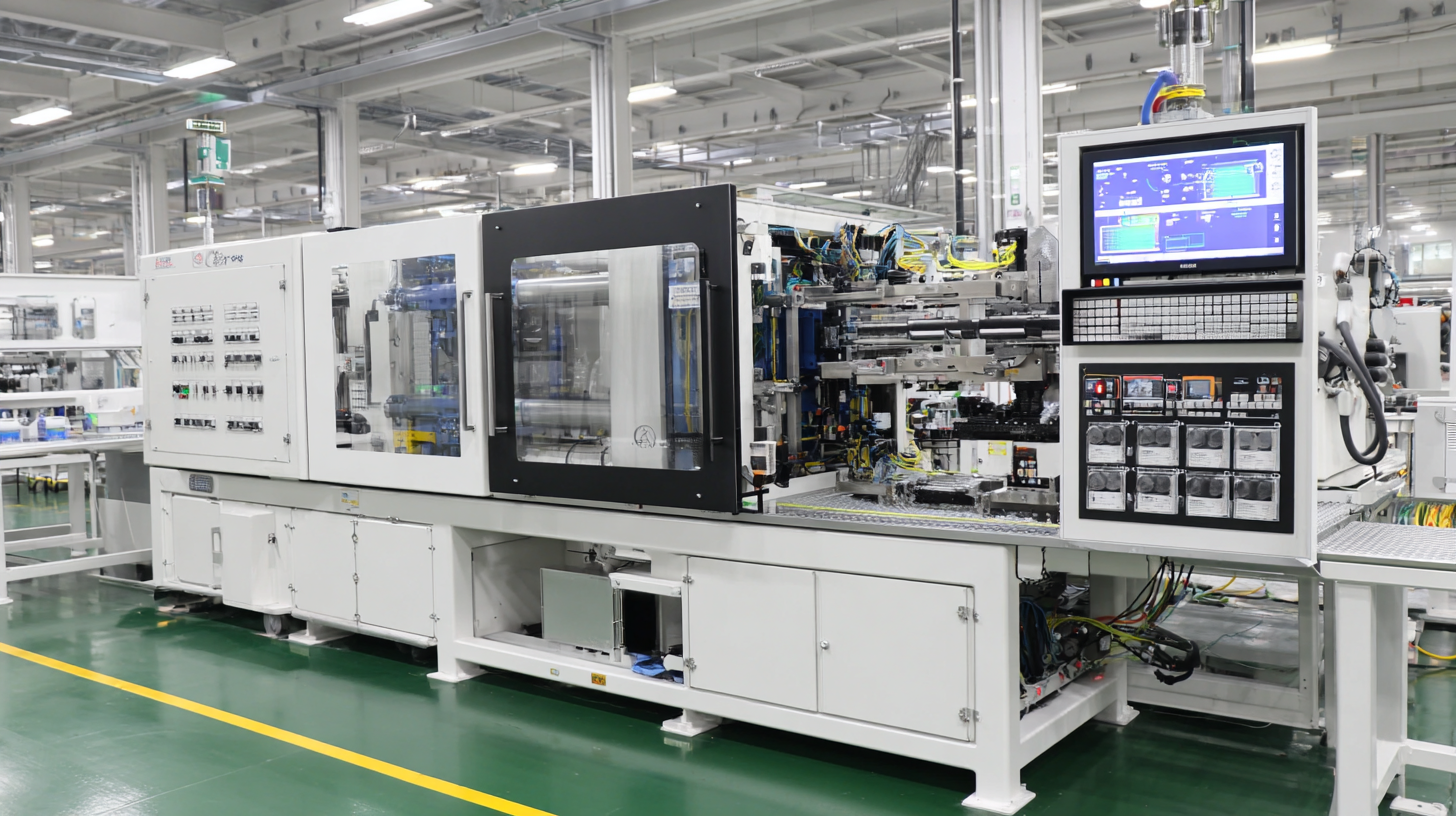

 Low pressure injection molding is a specialized manufacturing technique that offers several advantages, particularly in producing intricate components with fine details. Understanding the basics of this method begins with recognizing its operational principles. Unlike conventional high-pressure injection molding, low pressure techniques utilize lower force to inject molten material into a mold. This results in reduced mechanical stress on the components and can lead to fewer defects in the final product.
Low pressure injection molding is a specialized manufacturing technique that offers several advantages, particularly in producing intricate components with fine details. Understanding the basics of this method begins with recognizing its operational principles. Unlike conventional high-pressure injection molding, low pressure techniques utilize lower force to inject molten material into a mold. This results in reduced mechanical stress on the components and can lead to fewer defects in the final product.
One of the critical aspects of low pressure injection molding is the selection of appropriate materials. Thermoplastic elastomers and certain types of thermoplastics are often used due to their compatibility with this technique. Additionally, mastering the temperature and viscosity of the material is essential, as these factors directly influence the flow characteristics during molding. By controlling these variables, manufacturers can achieve a uniform fill and maintain dimensional accuracy, thereby optimizing both the quality and efficiency of their production processes. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for anyone looking to harness the benefits of low pressure injection molding successfully.
To effectively master low pressure injection molding techniques, understanding the essential equipment and materials is crucial. The primary equipment includes a low pressure injection molding machine designed specifically for handling lightweight materials at reduced pressure levels. This allows for enhanced control over the injection process, resulting in improved product quality and reduced cycle times. Additionally, using a precision temperature control system is vital to maintain optimal resin temperatures for consistent flow and to prevent defects.
When selecting materials for low pressure injection molding, it’s important to choose thermoplastic resins that are compatible with the specific application. For instance, materials like polypropylene and polyethylene are widely used due to their excellent flow characteristics and strength. Incorporating additives such as colorants and fillers can also enhance the performance of molded parts, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
**Tips:** Always ensure that the injection machine is calibrated correctly to optimize pressure settings. This can help prevent common issues such as incomplete filling or warpage. Moreover, consider conducting trial runs with different materials to identify which offers the best performance under low pressure conditions.
| Equipment/Material | Purpose | Specifications | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding Machine | To inject molten material into molds | Low pressure capability (below 150 psi) | Small to medium-sized parts |
| Mold | Shaping the injected material | Custom-designed to specific part dimensions | Precision components |
| Thermoplastic Material | To create parts through molding | Varies based on application (e.g., ABS, PC) | Consumer products, automotive parts |
| Temperature Control Unit | Maintaining optimal molding temperature | Temperature range 100-200°C | Any injection molding application |
| Cooling System | Cooling molds to solidify the material | Water or air-cooled systems | High-volume production runs |
Setting up a low pressure injection molding process requires careful planning and execution to achieve optimal results. Begin by selecting the right materials, as the choice of resin plays a critical role in the quality of the final product. Ensure that the material is compatible with low pressure techniques and is suitable for the intended application. Next, it is essential to calibrate your injection molding machine appropriately. Adjust the pressure settings to a level that allows for efficient filling of the mold without causing defects like short shots or excessive flash.
Once the machine is calibrated, focus on mold design and preparation. It is advisable to use molds that have been specifically engineered for low pressure applications, as they can help manage cooling and enhance product consistency. Additionally, maintain your molds regularly to avoid contamination, which can adversely affect the molding process. Finally, conduct test runs with your setup to refine parameters such as temperature, cycle time, and part ejection methods. Documenting these settings will help establish a reliable process that can be repeated to produce high-quality molded parts consistently.
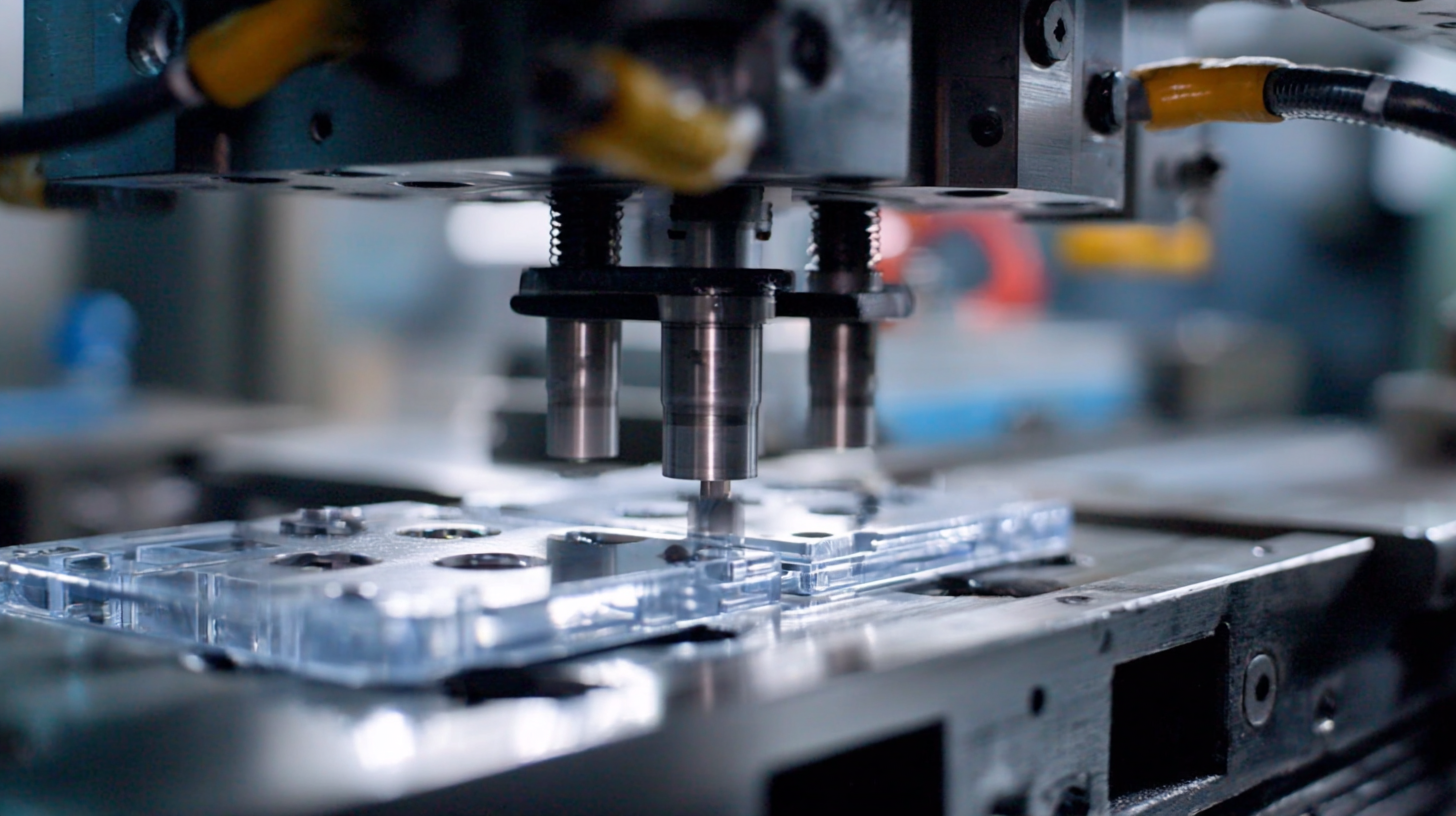 Low pressure injection molding offers various advantages in producing complex shapes with minimal defects, but it does come with its own set of challenges. One common issue is inconsistent material flow, which can lead to incomplete fills and dimensional inaccuracies. To address this, it is important to ensure proper heating of the material and the injection system, as well as to maintain optimal injection pressure and speed. Additionally, using the right gate design and optimizing the mold temperature can help achieve a uniform material distribution and reduce cycle times.
Low pressure injection molding offers various advantages in producing complex shapes with minimal defects, but it does come with its own set of challenges. One common issue is inconsistent material flow, which can lead to incomplete fills and dimensional inaccuracies. To address this, it is important to ensure proper heating of the material and the injection system, as well as to maintain optimal injection pressure and speed. Additionally, using the right gate design and optimizing the mold temperature can help achieve a uniform material distribution and reduce cycle times.
Another significant challenge is managing gas entrapment, which can cause defects such as voids or blisters in the final product. Proper venting in the mold design is crucial to facilitate the expulsion of trapped air. Incorporating strategically placed vents and controlling the injection speed can minimize the risk of gas entrapment. Furthermore, careful selection of raw materials with suitable viscosities can enhance flow characteristics, allowing for better filling and less air incorporation. By proactively addressing these challenges, manufacturers can improve the quality and efficiency of their low pressure injection molding processes.
To achieve optimal results in low pressure injection molding, it's essential to understand the critical factors that influence the process. First and foremost, selecting the right materials is crucial. Engineers should consider the viscosity and thermal properties of the polymer to ensure proper flow and cooling. Using additives can also enhance the material's performance, making it more suitable for low pressure applications. Additionally, controlling the temperature of both the mold and the injection material can significantly impact the finished product's quality.
Another best practice is to fine-tune the injection speed and pressure. Slower injection speeds can help minimize defects and optimize surface finish by allowing the material to fill the mold more uniformly. It's also important to monitor the cooling time and adjust it based on the part's geometry to avoid warping or residual stresses. Regular maintenance of the injection molding equipment ensures consistent performance, reducing the likelihood of defects and increasing productivity. Emphasizing these practices will lead to improved efficiency and quality in low pressure injection molding.






