Injection molding pressure plays a critical role in the manufacturing process. The right pressure can determine the quality of the final product. In 2026, industry experts are closely examining this factor.
Choosing the best injection molding pressure is not straightforward. Factors like material type and mold design can change optimal settings. Different applications may require different approaches, leading to extensive experimentation.
As technology evolves, so do the standards for pressure settings. Manufacturers need to stay updated to avoid defects. Balancing efficiency and quality remains a challenge. It’s an ongoing journey requiring constant reflection and adjustment.

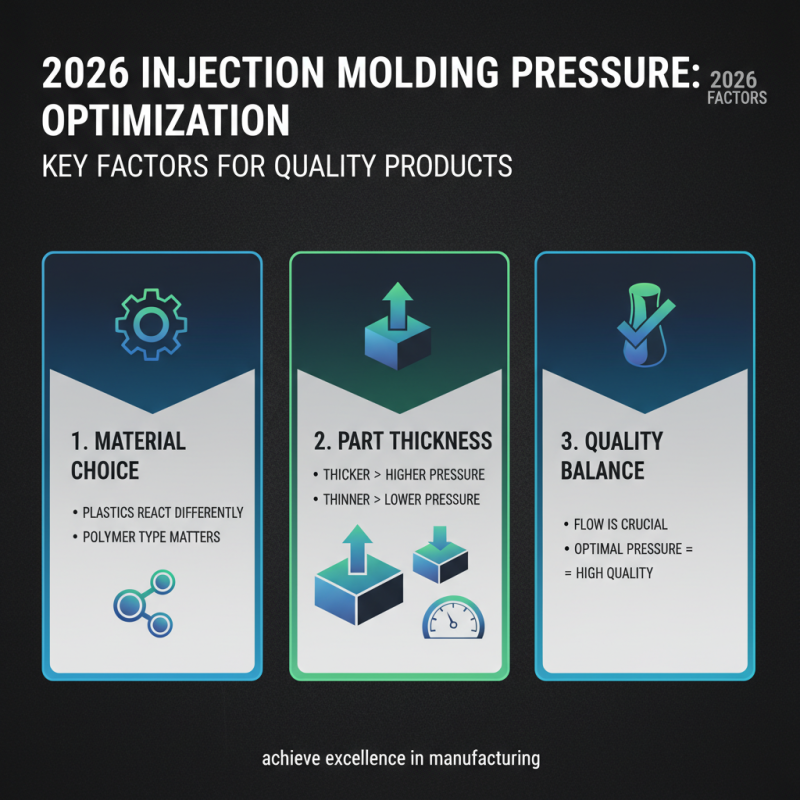
In 2026, determining the best injection molding pressure involves several key factors. Material choice plays a crucial role. Different plastics respond uniquely to pressure variations. Thicker materials may require higher pressures to flow properly. Conversely, thinner materials often need less. This balance is essential for achieving high-quality products.
Temperature also significantly influences injection molding pressure. As temperatures rise, material viscosity decreases. This phenomenon allows for lower injection pressure during the molding process. However, managing these temperatures can be challenging. Too high temperatures can lead to defects like warping. Operators must find an optimal range to avoid flaws.
Mold design is another pivotal aspect. The layout of gates, runners, and cooling channels must be precise. Imperfect designs may result in uneven pressure distribution. This inconsistency can lead to defects and wasted resources. Regular assessments of mold designs are necessary for improvement. Each project demands careful thought and adjustment. Mistakes can be costly, but they provide valuable learning opportunities.
In the world of injection molding, pressure plays a crucial role. The ideal pressure parameters can vary significantly based on the material used. Common materials like polypropylene, polystyrene, and ABS have different optimal settings. For instance, polypropylene typically requires lower pressure, while ABS might need higher. It’s important to adjust pressure based on the material's characteristics.
Understanding these parameters can be tricky. Too high pressure can lead to defects, such as flash or sink marks. Conversely, too low pressure may result in incomplete fills. Manufacturers often face challenges fine-tuning these settings for each material. Mistakes in pressure can lead to increased costs and wasted materials.
Experimentation is key. A standard setup seldom yields perfect results. Regularly reviewing and adjusting pressure settings is essential. Each production run may demand different fine-tuning. Being open to recalibrating processes can ultimately enhance product quality. This ongoing reflection will lead to better outcomes over time.
| Material Type | Optimal Injection Pressure (MPa) | Melt Temperature (°C) | Cycle Time (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | 60-90 | 200-250 | 15-25 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 50-80 | 220-260 | 10-20 |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 80-100 | 220-240 | 20-30 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 60-90 | 200-230 | 15-25 |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | 70-110 | 180-210 | 20-35 |
In 2026, the importance of injection speed in molding processes cannot be overstated. Higher injection speeds can lead to better filling of complex mold cavities, reducing the risk of defects. However, this comes with elevated pressure requirements. Operators must carefully balance these factors to achieve optimal results.
Pressure levels must match the required injection speed. If the speed is too high without adequate pressure, it can result in incomplete fills or air entrapment. If the pressure is too high, materials may degrade. Experimentation is key. Each material behaves differently under varying speeds and pressures. Understanding these nuances is crucial for production efficiency.
Monitoring the relationship between injection speed and pressure should be a priority. Variations can cause unexpected results, and it's essential to remain vigilant. Adjustments may be necessary based on environmental conditions and material behavior. Continuous learning and adaptation will help refine processes, achieving better quality products in the long run.
The world of injection molding is evolving. As we approach 2026, advancements in technology are shifting how manufacturers view pressure settings. Efficient energy use and improved material quality are driving changes. New sensors and automation tools allow for tighter control over processes. This precision can lead to reduced waste during production.
However, adjusting pressure settings also brings challenges. Not all materials respond uniformly under varying pressures. Some may warp or fail to fill molds properly. Manufacturers need to test and retest to find the sweet spot. This might slow down production initially but can yield better results later on. The pressure that worked last year may not suffice today.
Moreover, industry standards are continually changing. Innovations like 3D printing and advanced polymers can alter pressure requirements. Companies must stay informed. They must adapt to maintain competitive edges while ensuring the quality of the end product. Investing time in research and development can seem daunting but is often necessary.
In the quest for optimal injection molding pressure, looking back at previous years is vital. Data from industry reports indicates that pressure settings have gradually evolved. In 2020, the average pressure was around 900 to 1,200 psi. By 2023, there was a noticeable increase to approximately 1,100 to 1,400 psi. This shift shows manufacturers adapting to the growing complexities of materials and designs.
As we approach 2026, many industry experts predict that pressure settings might climb further. Some forecasts suggest an average of 1,300 to 1,600 psi could become standard. However, this brings challenges. Higher pressure can lead to defects like warping or sink marks. It is critical to balance pressure with cycle time optimization. Many manufacturers struggle with this, often compounding issues without proper adjustments.
Data from recent surveys reveal over 40% of companies reported issues rooted in pressure mismanagement. Adjusting pressures without fully understanding the implications can lead to costly errors. Not all materials respond the same way under high pressure. Each polymer’s unique characteristics can influence the outcome. Learning from past data is essential in navigating these complexities as pressure settings evolve.