The rise of automated machines is reshaping industries rapidly. A recent report from the International Federation of Robotics noted that the global market for these machines is expected to reach $166 billion by 2025. This surge reflects a shift towards efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Companies are adopting automation in manufacturing, logistics, and retail to improve productivity and reduce human error.
Experts like Dr. Emily Sanders, a leading authority in robotics, emphasize, "Automated machines are not just tools; they are essential partners in innovation." This statement underscores the transformative role these machines play today. They enhance production speeds and improve quality control. However, the transition isn't smooth for all businesses. Smaller companies often face challenges in integrating these technologies and may struggle to compete.
Moreover, concerns about job displacement persist. While automated machines create new roles, many fear they may also eliminate existing ones. This ongoing debate raises questions about the balance between technology and human employment. As automated machines continue to revolutionize industries, we must reflect on both their benefits and drawbacks for a sustainable future.
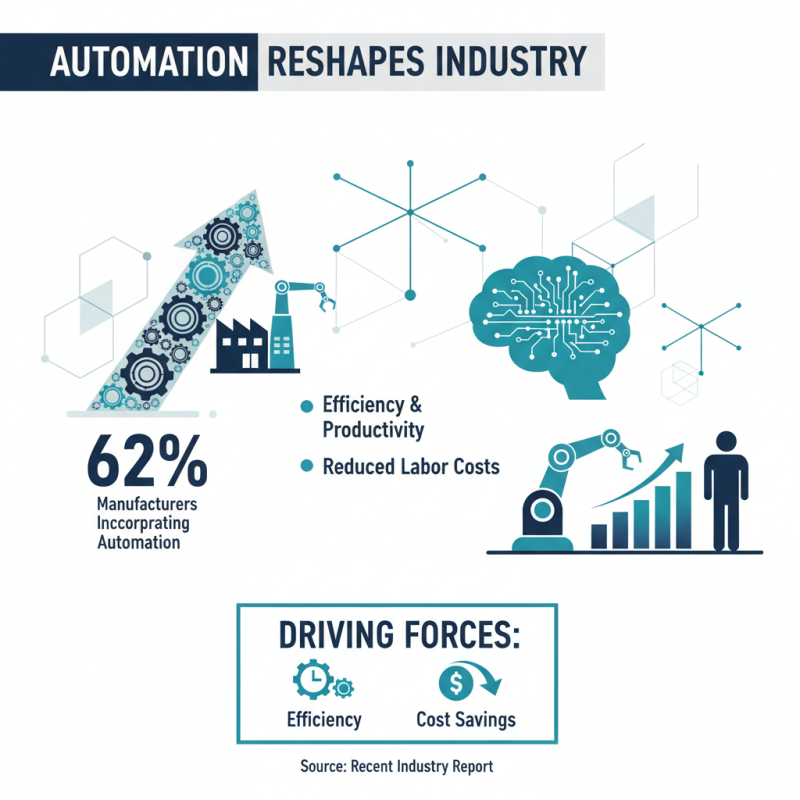
The landscape of modern industries is witnessing a significant transformation due to the rise of automated machines. For instance, a recent report indicates that 62% of manufacturers are incorporating some level of automation in their operations. This shift is not merely a trend but a necessity in today’s competitive environment. Labor costs and the need for efficiency are driving this change.
Automation brings notable advantages. According to industry data, automated processes can increase production speed by up to 30%. This means that tasks once requiring hours can now be completed in minutes. However, this tech revolution is not without concerns. Workers face displacement, with predictions suggesting that 20 million manufacturing jobs could be lost to automation by 2030. This reality prompts a deeper reflection on workforce adaptability.
While automated machines enhance precision and consistency, they also highlight gaps in skill development. A shocking 70% of companies report difficulty finding workers with the right tech skills. As industries lean heavily into automation, the challenge remains: how to upskill the existing workforce? The transformation brought by automation is significant, yet it requires careful navigation to ensure societal and economic stability.
Automation is reshaping industries at a rapid pace. The benefits for business efficiency are too significant to ignore. According to a report by McKinsey, implementing automation can increase productivity by up to 40%. This change allows companies to spend less time on repetitive tasks. Workers can focus on more strategic, creative activities.
Notably, automation can reduce costs significantly. A study from Deloitte highlights that businesses can save up to 30% in operational costs through automation. These savings facilitate reinvestment in innovation. However, organizations must address the human element in this transition. Automation may lead to job displacements. Companies need to rethink workforce strategies and offer retraining programs.
Moreover, quality control improves with automated systems. A survey from the International Federation of Robotics indicates that automation reduces error rates by around 50%. Yet, this reliance on technology requires constant maintenance and oversight. Industry leaders must ensure robust systems are in place. Adopting automation is not without its challenges, but the potential efficiency gains can drive substantial growth.
Automation is rapidly changing labor markets across the globe. Various industries are adopting automated machines to enhance efficiency and productivity. This shift impacts job availability and workforce dynamics. Many routine tasks are now performed by machines, leading to declines in certain job sectors. Workers in manufacturing and data entry roles face increased competition from automation.
However, the transition is not seamless. Some workers struggle to adapt to new technology. Job displacement raises concerns about economic stability and personal livelihoods. The move towards automation can create a skills gap, leaving many underprepared for the new landscape. There is a growing need for retraining programs to help displaced workers find new opportunities in evolving industries.
The rise of automation also invites questions about the nature of work itself. Are jobs solely defined by their tasks? As machines take over, some roles will change fundamentally. Workers may need to focus on creativity and interpersonal skills. This shift could lead to a workforce that values adaptability and continuous learning. Industries must consider how to integrate automation while supporting their employees through this transition.
Automated machines are reshaping industries everywhere. Technological innovations are at the forefront of this transformation. Robotics and artificial intelligence are enabling precision and efficiency. These machines complete tasks faster than humans. In factories, robots handle assembly lines. They reduce manual labor and errors, which makes production smoother.
However, this shift raises some concerns. Job displacement is a real issue. Many workers fear losing their jobs due to automation. Also, not all automated systems are flawless. Occasionally, machines malfunction or misread data. This can lead to costly mistakes in operations. Companies must weigh the benefits against potential challenges.
Furthermore, ethical considerations around data privacy arise. As machines learn from data, who owns that information? Striking a balance between innovation and responsibility is crucial. Questions about equity in the workplace continue to surface. Ultimately, as industries evolve, society must adapt alongside them.
The automation trend significantly impacts various industries. Manufacturing is one of the most affected fields. Automated machines streamline production processes, reducing human error. This results in faster output and lower costs. However, the workforce often feels threatened. Many workers worry about job security in an automated world.
Another industry changing is agriculture. Automation in farming enhances efficiency. Drones monitor crops, while robots assist with planting and harvesting. This boosts productivity but can leave seasonal workers without jobs.
Striking a balance is crucial here. Technology should support human efforts, not replace them.
Tips: When embracing automation, consider worker retraining. Help them adapt to new technologies. Create a supportive environment that encourages skill development. Stay aware of the ethical implications. Automation can create opportunities while leading to displacement. Regular communication helps ease transitions.






